Technology
3D Printing Innovation
3D printer technology
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM)
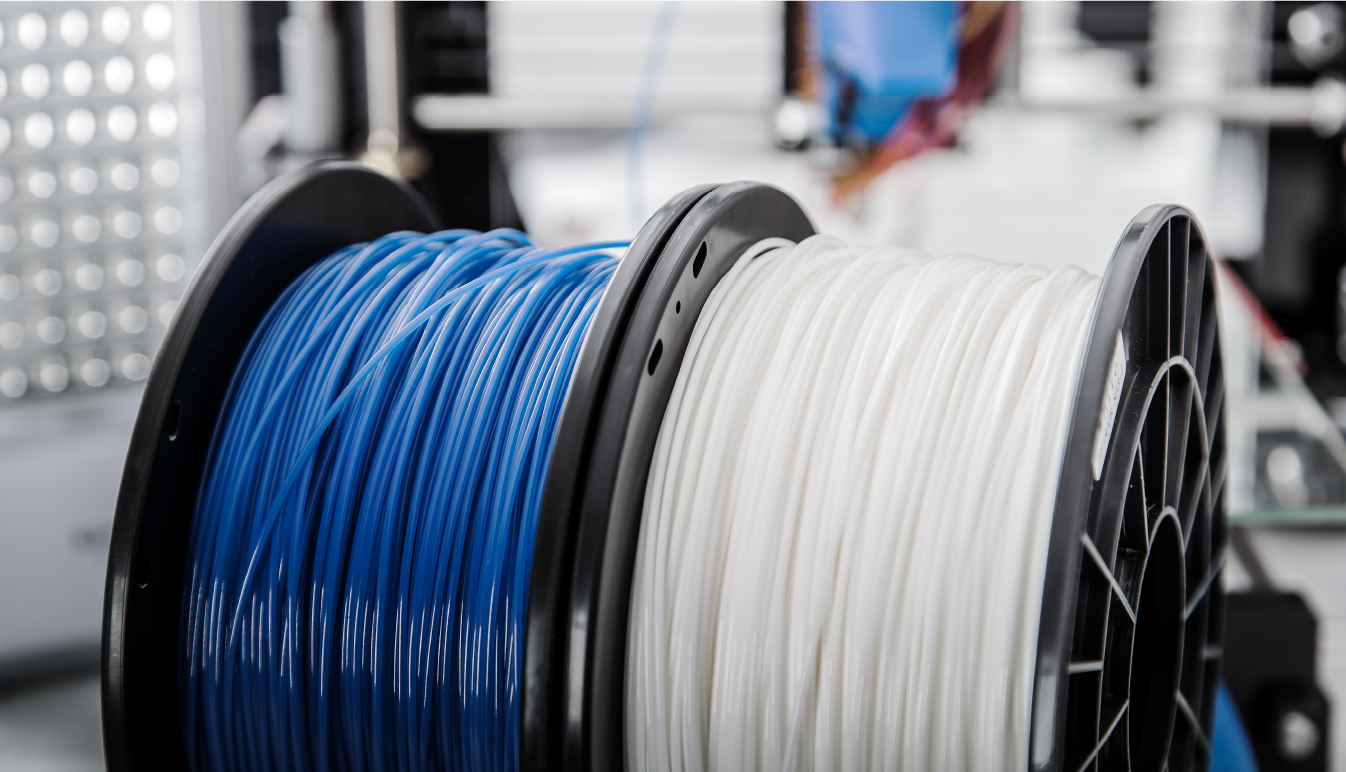
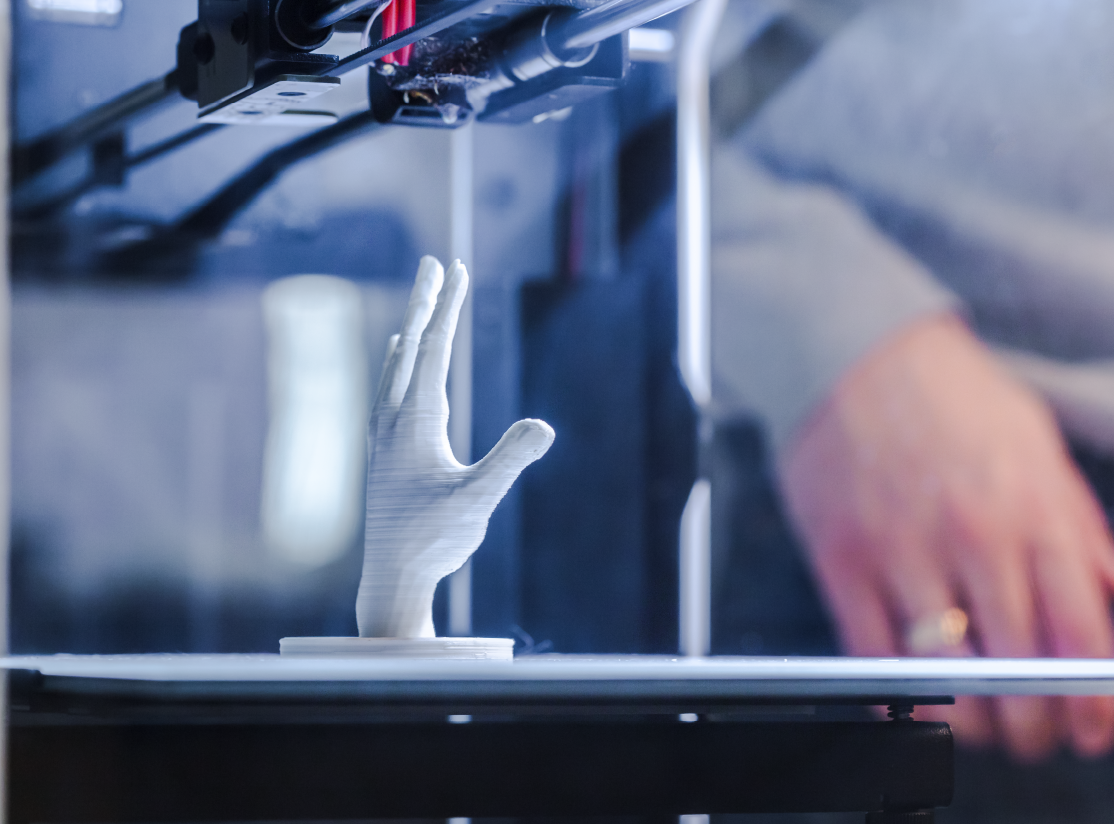
This forming system is widely recognized for its ease of use, with a variety of materials employed in the printing process according to the applications. In most cases, thermoplastics are used for the molding of workpieces. The printing material, referred to as filament, is introduced into the system via an extrusion motor, where it is subsequently directed to the melting area and extruded through a nozzle. The workpiece is then created layer by layer, following the mechanical design specifications. This system is designed for engineering applications, including both prototype development and production of finished goods for commercial purposes.


Stereolithography and
Digital Light Processing (SLA&DLP)
This system offers high-precision forming, making it well-suited for medical and industrial applications, including the production of prototypes. The printing material utilized in this process is a liquid plastic that solidifies upon exposure to ultraviolet (UV) light at wavelengths between 400 and 410 nm. However, a noted limitation of this system is the relative weakness of the finished workpiece.
Selective Laser Sintering (SLS)
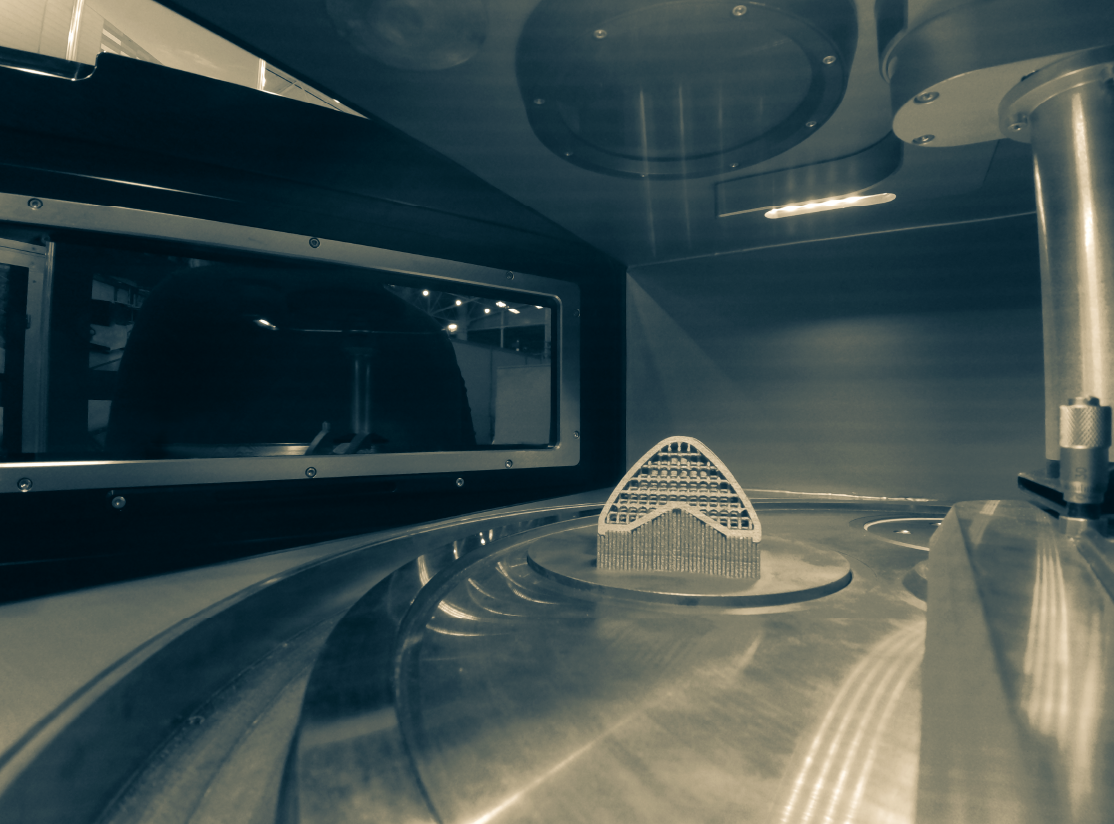
The process utilizes heat from a laser to fuse powder-based printing materials. When the powder is exposed to the laser for a specified duration, sintering occurs, causing the particles to bond and form exceptionally strong, high-precision components. The precision is attributed to the use of a finely focused laser beam.