3D Filament
Currently, the use of 3D printing technology is becoming increasingly prevalent across diverse sectors, including industry, education, and healthcare. This innovative technique facilitates the rapid creation of complex and customizable prototypes, such as skulls and other human organs, which serve as valuable educational tools for medical students before engaging in actual surgical operations. In fused deposition modeling (FDM) system, the utilized materials are termed 3D filament. This encompasses a variety of plastic filaments with distinct properties tailored to specific applications.
ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene)

Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene (ABS) is a fundamental material employed in Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) 3D printing, distinguished by its exceptional mechanical properties. ABS exhibits considerable toughness and flexibility, enabling the production of components capable of withstanding substantial pressure and bending forces. As such, it is particularly well-suited for engineering applications and can endure temperatures of up to 100 degrees Celsius, making it applicable in industrial machinery settings. Furthermore, ABS facilitates processes such as drilling, threading, polishing, and painting more effectively than other filament materials.
Advantages and disadvantages of ABS
Advantages:
- Excellent resistance to bending (flexural strength) and impact.
- Easily polished, painted, and threaded.
- Temperature resistance ranging from 90 to 100 degrees Celsius.
Disadvantages:
- Emission of unpleasant odors during processing.
- Limited resistance to ultraviolet (UV) light.
PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate with Glycol)
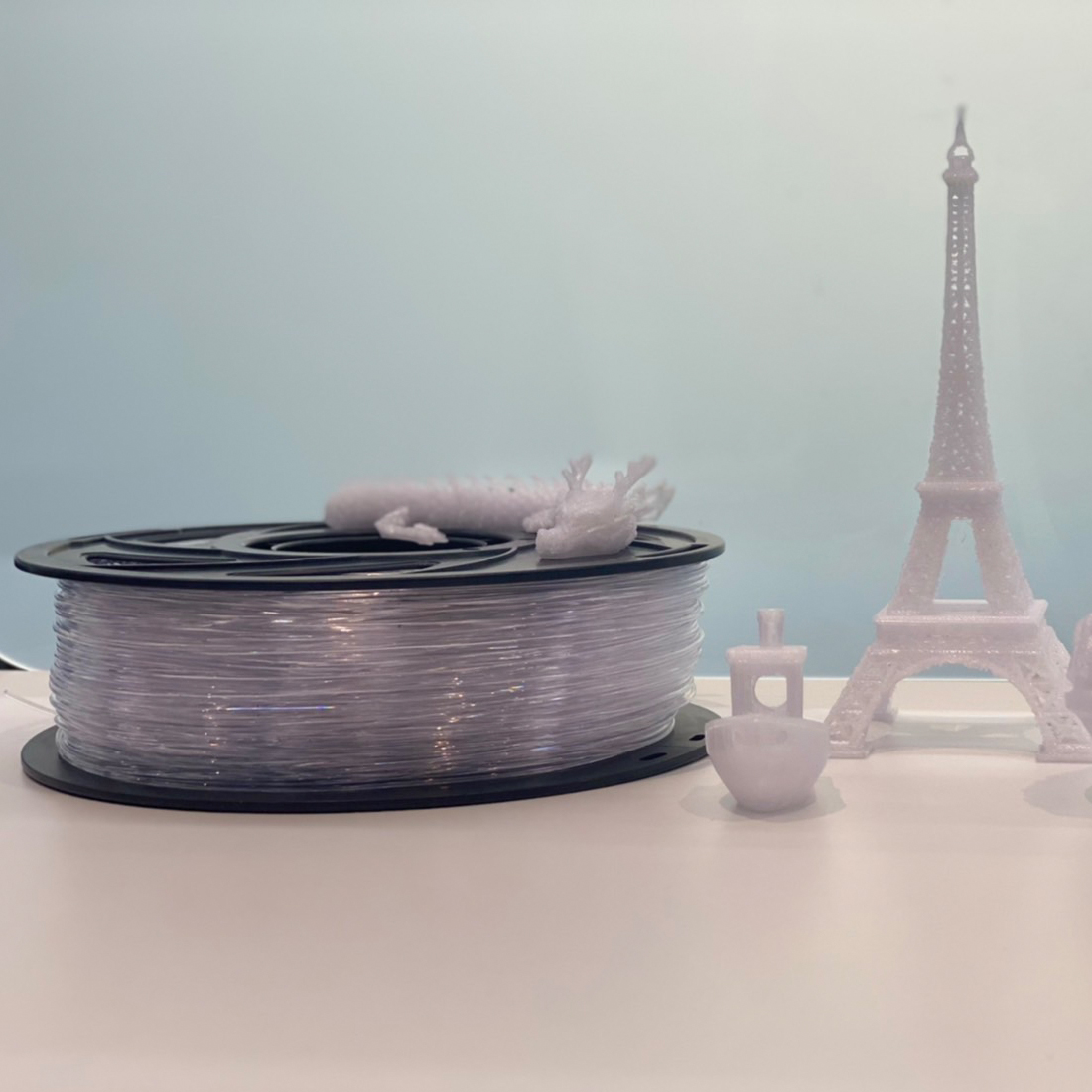

PETG (Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol-Modified) is a material synthesized from PET (Polyethylene Terephthalate) that is primarily utilized in the manufacture of drinking water bottles. The incorporation of glycol enhances the material's clarity and viscosity, thereby facilitating its suitability for 3D printing processes.
Advantages and disadvantages of PETG
Advantages:
- Exhibits greater toughness than ABS while demonstrating slightly lower flexural strength.
- Standard-grade PETG can withstand temperatures ranging from 75 to 80 degrees Celsius.
- Display resistance to acidic and alkaline environments.
- Feature a transparent base, making it suitable for applications such as lamp manufacturing and electronic components that require visibility.
Disadvantages:
- More challenging to polish and paint compared to PLA and ABS.
PC (Polycarbonate)

Polycarbonate (PC) is an exceptionally versatile material that finds application across various industries, including automotive, electronics, construction, and healthcare, owing to its outstanding properties, which include high strength and robust resistance to acids, alkalis, chemicals, and elevated temperatures.
Advantages and disadvantages of PC
Advantages:
- Exhibit remarkable toughness and strength, with significant resistance to bending.
- Capable of withstanding prolonged exposure to temperatures of up to 120 ºC and short-term applications at temperatures reaching 140 ºC.
- Provide excellent resistance to both acidic and alkaline environments.
- Transparent in nature, allowing for effective light transmission.
Disadvantages:
- Require higher processing temperatures than standard filaments, rendering it incompatible with conventional 3D printers.
- Exhibit a tendency to absorb moisture from the surrounding environment; therefore, it is advisable to store it in a sealed cabinet and subject it to drying before use.