Technology
Our Technology

ZnO Nano
For Agriculture
Develop innovative zinc oxide powder to reduce size with nanotechnology to contain nanometer particles
3D Printing
Technology
Create 3D shapes to support
industrial applications medical parts
Our Technology






IRPC has invented a new product, "Bio-based polystyrene", under the brand POLIMAXX, grade PK150B20. This bio-based polystyrene plastic contains 20% natural ingredients, reducing the reliance on fossil-based materials. This makes it an eco-friendly product, 100% recyclable, and aligned with green practices.
The natural materials used in its production come from cassava, a crop grown by Thai farmers. This initiative not only helps support farmers but also promotes the country's economy. Furthermore, this product is protected by petty patents from the Department of Intellectual Property. This polymer can be molded using injection molding to create items such as spoons, forks, knives, and trays. It has been tested to meet food contact standards (EU No 10/2011 and US FDA 21 CFR 177.1640), assuring consumers that it is safe for food-related use. Additionally, it can be molded into various products suitable for modern lifestyles, such as plant pots and eco-friendly office supplies. The new generation, with their modern, convenient lifestyles, is increasingly concerned about the environment. The use of environmentally friendly products, like bio-based polystyrene plastic made from natural materials and fully recyclable, contributes to sustainable efforts to protect our planet.
The problem of global warming is increasing day by day, leading to significant changes in the natural environment. IRPC Public Company Limited recognizes the urgency of this situation and has committed to designing and developing products aimed at addressing environmental challenges. Bio-based polypropylene is an innovation that incorporates natural materials to reinforce polypropylene, making the product more environmentally friendly. This product is designed with the 3Rs principle in mind—Reduce, Reuse, Recycle—to contribute to environmental conservation. It contains up to 30% natural materials, reducing the reliance on polypropylene (Reduce) and lowering greenhouse gas emissions from the polypropylene production process. The product can be reused multiple times and is recyclable. Additionally, it has passed the overall migration food contact tests in compliance with EU 10/2011 and US FDA 21 CFR 177.1520 (Olefin Polymers), ensuring that consumers can confidently choose products that are not only eco-friendly but also safe for food contact applications.



In today's world, one of the most prominent global trends is the growing emphasis on environmental sustainability and awareness. As consumers become increasingly mindful of the environmental impact of various products, particularly those made from plastics or polymers, the demand for eco-friendly solutions continues to rise. During the production of ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) products, it is virtually impossible to achieve a fully complete chemical reaction, which can lead to the emission of toxic volatile substances that may adversely affect both human health and the environment.
In response to these challenges, IRPC Public Company Limited has developed ABS products with Low VOCs (Volatile Organic Compounds), significantly reducing the release of harmful emissions. This innovation ensures that these products are safer for both human health and the environment.


Disinfection is essential in the production of tap water for consumption. This can be accomplished through various methods, including the use of ultraviolet light, ozone, and chemical agents. Among these methods, chlorine's application for tap water disinfection is widely adopted across all water supply systems. word
Chlorine, being an oxidizing agent, has the potential to corrode materials, including HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene) plastic pipes, particularly when employed over extended periods. Consequently, this can lead to a reduction in the lifespan of HDPE pipes. Thus, the development of pipes with chlorine-resistant properties is of considerable interest. In this regard, IRPC Public Company Limited has engineered high-quality HDPE PE100 pipe-grade resin. This resin is characterized by a polymer structure designed for optimal moldability and exceptional strength. The research team has also developed an additive formulation that enhances the resin's resistance to degradation and corrosion by chlorine during the transportation of chlorinated water. These chlorine-resistant pipes are available in two colors: black and blue.
Key features of innovation
- Compliance with ISO and ASTM standard
- Extension of pipe service life by up to three times
- Capability to transport water with high chlorine content
- High moldability and mechanical strength

The HDPE PE100 chlorine-resistant pipe effectively facilitates the transport of chlorinated water, significantly extending its service life. It is well-suited for the conveyance of both drinking water and tap water. Furthermore, this grade of plastic resin is not only easily moldable but also robust, meeting stringent international standards.



Product Features & Benefits
• High elasticity and mechanical properties akin to rubber.• Capable of being molded using various plastic processing methods, including injection molding and extrusion.
• Heat resistance ranging from 120 to 150 degrees Celsius.
• Material hardness can be tailored according to specific application requirements.
• Incorporates natural rubber in the production process, yielding environmentally friendly products.
• Recyclable
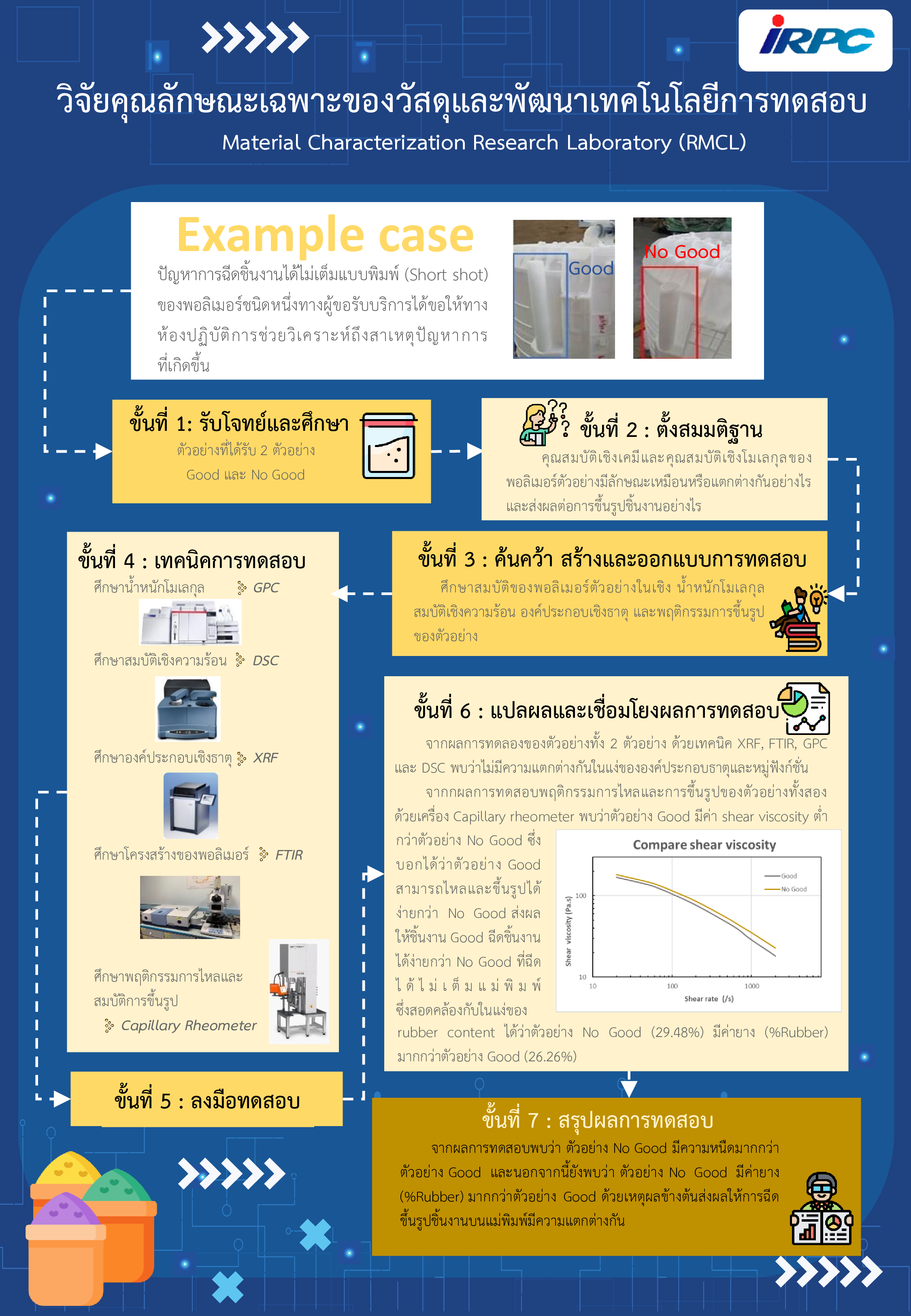
 Currently, the heavy industrial and marine paint sectors play an indispensable role across various industries. The economic growth rate remains steady, and there is an ongoing expansion of investment into international markets. However, the leading company still faces product-related challenges. Feedback from experienced users highlights persistent issues with chemical and environmental resistance in paints designed for heavy industry and marine applications.
In response to these challenges, IRPC Public Company Limited has developed advanced products to effectively address these pain points. Utilizing technology based on the company's Anti-Dripping additive—a polymer additive developed with nanotechnology that prevents polymer dripping upon ignition—IRPC has created a solution with optimal dispersibility in polymers. When applied to heavy industrial and marine paints, this innovation yields a product with superior resistance to weathering and seawater corrosion for over 1,000 hours, as well as robust resistance to both acidic and alkaline environments. Furthermore, it withstands abrasion and impact stresses exceeding 2 kilograms per cubic meter. This development significantly enhances the durability and performance of heavy industrial and marine paints, positioning IRPC’s products as comparable to or exceeding the quality of leading products on the market.
Currently, the heavy industrial and marine paint sectors play an indispensable role across various industries. The economic growth rate remains steady, and there is an ongoing expansion of investment into international markets. However, the leading company still faces product-related challenges. Feedback from experienced users highlights persistent issues with chemical and environmental resistance in paints designed for heavy industry and marine applications.
In response to these challenges, IRPC Public Company Limited has developed advanced products to effectively address these pain points. Utilizing technology based on the company's Anti-Dripping additive—a polymer additive developed with nanotechnology that prevents polymer dripping upon ignition—IRPC has created a solution with optimal dispersibility in polymers. When applied to heavy industrial and marine paints, this innovation yields a product with superior resistance to weathering and seawater corrosion for over 1,000 hours, as well as robust resistance to both acidic and alkaline environments. Furthermore, it withstands abrasion and impact stresses exceeding 2 kilograms per cubic meter. This development significantly enhances the durability and performance of heavy industrial and marine paints, positioning IRPC’s products as comparable to or exceeding the quality of leading products on the market.
 At the international level, interest has emerged in addressing environmental concerns associated with lubricants by advancing the development of biodegradable alternatives. These lubricants are derived from natural, renewable raw materials, such as vegetable oils or animal fats, classified within the Oleochemical group. Certain petroleum-derived oils can also serve as starting materials. Lubricants of this nature are categorized as natural esters. However, specific attributes of natural esters, such as pour point and oxidative stability, are often insufficient for the stringent demands of modern machinery, rendering them less effective than petroleum-based lubricants.
To address these limitations, the Petroleum Product Research and Development Group, along with the Specialty Products Division, has concentrated on synthetic ester lubricants. These synthetic esters not only share a similar chemical structure to natural esters but are also biodegradable. Moreover, synthetic esters offer the distinct advantage of customizable molecular design, enabling manufacturers to engineer specific characteristics that meet functional requirements precisely. As a result, synthetic esters exhibit superior application performance compared to petroleum-based lubricants.
At the international level, interest has emerged in addressing environmental concerns associated with lubricants by advancing the development of biodegradable alternatives. These lubricants are derived from natural, renewable raw materials, such as vegetable oils or animal fats, classified within the Oleochemical group. Certain petroleum-derived oils can also serve as starting materials. Lubricants of this nature are categorized as natural esters. However, specific attributes of natural esters, such as pour point and oxidative stability, are often insufficient for the stringent demands of modern machinery, rendering them less effective than petroleum-based lubricants.
To address these limitations, the Petroleum Product Research and Development Group, along with the Specialty Products Division, has concentrated on synthetic ester lubricants. These synthetic esters not only share a similar chemical structure to natural esters but are also biodegradable. Moreover, synthetic esters offer the distinct advantage of customizable molecular design, enabling manufacturers to engineer specific characteristics that meet functional requirements precisely. As a result, synthetic esters exhibit superior application performance compared to petroleum-based lubricants.
 Synthetic ester oils, developed commercially by manufacturers, serve as highly effective, naturally biodegradable lubricants suitable for modern machinery. These environmentally sustainable products offer concrete benefits by mitigating adverse impacts on natural ecosystems, environmental health, communities, and living organisms. Furthermore, utilizing renewable natural raw materials decreases dependency on imported crude oil and contributes to economic development within the agricultural sector.
Synthetic ester oils, developed commercially by manufacturers, serve as highly effective, naturally biodegradable lubricants suitable for modern machinery. These environmentally sustainable products offer concrete benefits by mitigating adverse impacts on natural ecosystems, environmental health, communities, and living organisms. Furthermore, utilizing renewable natural raw materials decreases dependency on imported crude oil and contributes to economic development within the agricultural sector.Biodiesel, also known as B100 or chemically as Fatty Acid Methyl Ester (FAME), is utilized as an additive in diesel fuel derived from refined crude oil, blended in accordance with specifications and quality standards mandated by the Department of Energy Business under the Ministry of Energy. This blend is distributed as high-speed diesel fuel through petrol stations in Thailand. Refineries are required to source biodiesel from domestic producers who meet stringent quality criteria established by the Department of Energy Business. Prior to acceptance, biodiesel is tested including assessments of water content, viscosity index, and visual inspections for clarity and sediment. Nevertheless, quality inconsistencies have been observed in certain biodiesel batches from manufacturers. When incorporated into diesel fuel, these batches have occasionally exhibited phase separation between foam and diesel within storage tanks, leading to complications in fuel transfer systems and operational issues in the fuel supply mechanisms of diesel engines.
Therefore, the petroleum products and specialty products R&D team together with the material characterization research team and development of testing technology jointly research and use analytical techniques to identify foreign substances in biodiesel that cause Thermo gravimetric analysis (TGA), Scanning electron microscopy and energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (SEM-EDS) and Gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy (GC-MS) techniques can identify contaminants in vapor oil. Dodiesel is an organic Sterol glucoside, which can be either Free steryl glucoside or in the form of Acylated steryl glucoside. These two organic compounds, if in pure form, are white. has a high melting point of more than 200 ˚ C . Therefore, if in the biodiesel production process, these two organic compounds are not completely removed and then used as an additive to the finished high speed diesel fuel. It can cause problems for users in diesel engines, such as clogging in the car's fuel filter. Blockage in fuel injectors, etc.

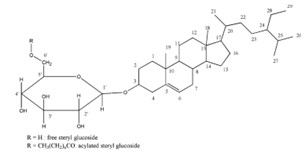
(References: Van Hoed, V., Zyaykina, N., De Greyt, W., Maes, J., Verhé, R., & ; Demeestere, K. (2008). Identifi. cation and occurrence of steryl glucosides in palm and Soy Biodiesel. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society, 85(8), 701–709. )
Furthermore, prior research indicates that sterol glucosides are naturally present in vegetable oils. During the transesterification process under alkaline conditions to produce biodiesel, acylated steryl glucosides within the sterol glucoside group are increasingly prone to conversion into free steryl glucosides.
Consequently, these advanced analytical techniques have been developed to detect organic sterol glucosides in biodiesel products provided by suppliers. This capability allows refineries to significantly reduce potential quality issues, mitigate risks, and address consumer complaints related to high-speed diesel fuel, thereby fostering enhanced credibility among consumers."
Styrenics polymer additives
SAG is a polymer blend utilized as a binder containing epoxy functional groups, with its binding efficiency determined by the concentration of epoxy groups within the polymer composition. These epoxy groups are capable of reacting with carboxyl, hydroxyl, or amide groups, making SAG effective as a linker between polymer blends such as PC/ABS and PA/ABS. Additionally, SAG serves as a chain extender, maintaining the integrity of heat-affected molecular chains to preserve polymer strength even after repeated thermal processing. This characteristic mitigates common drawbacks in plastic recycling within the plastics processing industry, supporting the use of SAG to prevent polymer degradation during heat exposure
Reaction mechanism
Example of the interaction mechanism between epoxy and hydroxyl groups at the chain end of the polyester molecular chain.
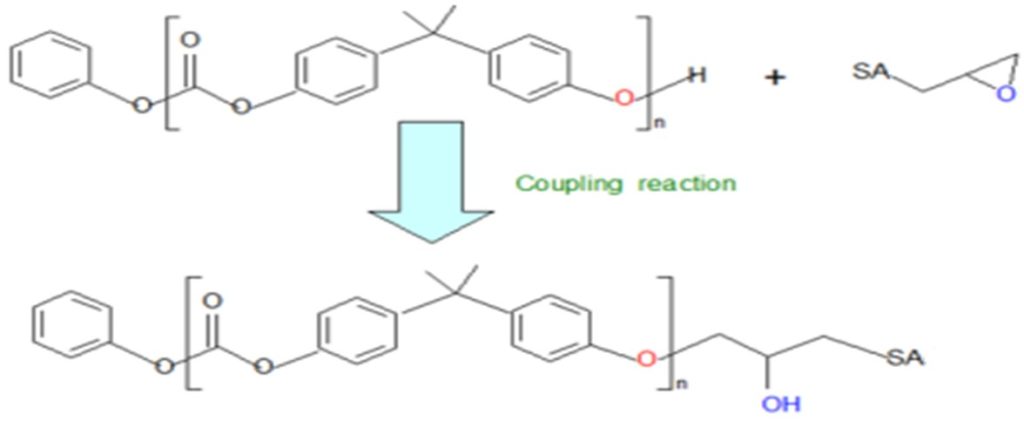
Chemical composition
SAG is a copolymer between styrene acrylonitrile and glycidyl methacrylate.
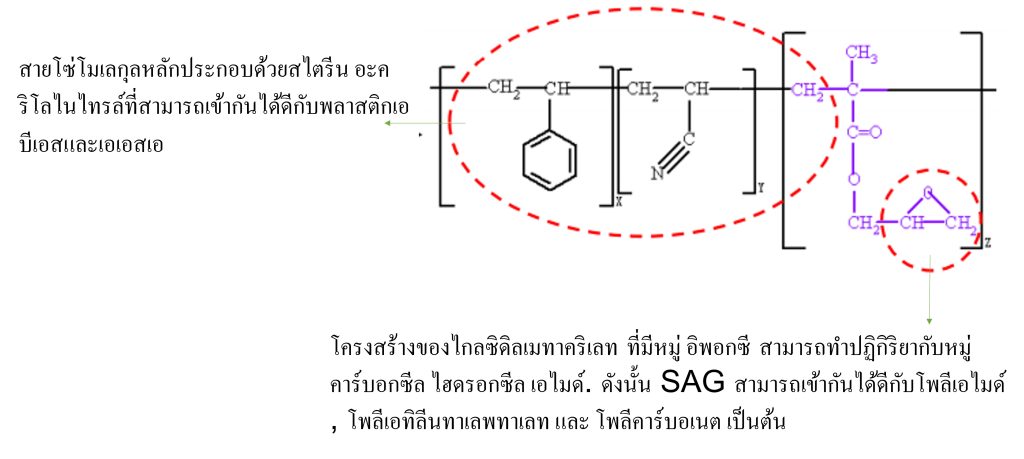
Synthesized SAG through suspension polymerization reaction


